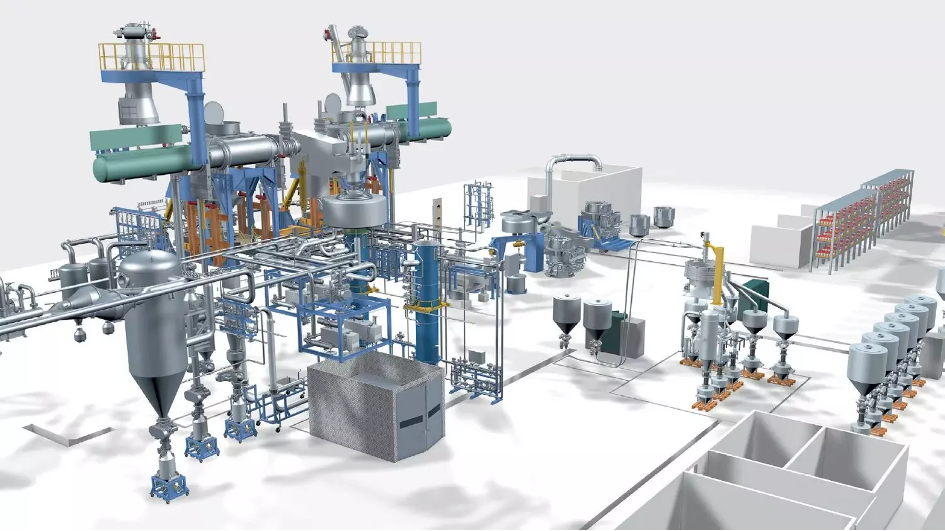
Revolutionizing Powder Production: The Power of Powder Atomizer Plants
In the world of powder production, powder atomizer plants stand as cutting-edge facilities that have revolutionized the manufacturing process. These plants play a crucial role in producing various types of powders, such as metal powders, alloy powders, ceramic powders, and more. In this blog post, we will explore the significance of powder atomizer plants, their operations, and their immense contribution to diverse industries.
Unveiling Powder Atomizer Plants:
Powder atomizer plants are advanced manufacturing facilities that utilize atomization technology to produce fine powders. Atomization involves breaking a liquid or molten material into droplets, which then solidify to form individual powder particles. These plants employ specialized equipment and processes to achieve precise control over particle size, morphology, and composition.
The Operations of Powder Atomizer Plants:
Let’s delve into the key operations within a typical powder atomizer plant:
- Material Preparation: The process begins with the preparation of the material to be atomized. This could involve melting a metal or heating a liquid precursor to a specific temperature and composition. The material is carefully chosen based on the desired powder properties and the specific requirements of the industry it serves.
- Atomization: Atomization is the heart of the powder atomizer plant. The prepared material is atomized using various techniques such as gas atomization, water atomization, or centrifugal atomization. These methods involve subjecting the material to high-pressure gas, a high-velocity liquid stream, or centrifugal forces, resulting in the formation of droplets that rapidly solidify into powder particles.
- Solidification and Collection: After atomization, the droplets solidify into fine powder particles as they cool down. The solidified particles are then collected using specialized systems such as cyclone separators or filters. The collection process ensures the separation of the powder from any residual gas or liquid, resulting in high-purity powders.
- Post-Treatment and Quality Control: Depending on the application requirements, the collected powder may undergo post-treatment processes such as sieving, heat treatment, or surface modification to further enhance its properties. Quality control measures are also implemented to ensure that the produced powders meet the desired specifications and industry standards.
Applications of Powder Atomizer Plants:
Powder atomizer plants have diverse applications across various industries:
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Powder atomizer plants produce metal powders with precise particle size and composition, making them ideal for additive manufacturing processes like 3D printing. These powders serve as the raw material for creating complex components in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare.
- Powder Metallurgy: Powder atomizer plants play a crucial role in the production of metal and alloy powders used in powder metallurgy processes. These powders are compacted and sintered to create high-performance components for applications in automotive, industrial machinery, and tooling industries.
- Coating and Surface Treatment: Powder atomized powders find application in coatings and surface treatments, providing enhanced properties such as wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and thermal protection. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and energy rely on these coatings to improve the performance and durability of their products.
- Ceramics and Advanced Materials: Powder atomizer plants produce ceramic powders used in the fabrication of advanced ceramics, electronic components, and cutting-edge materials. These powders possess controlled particle size, purity, and composition, ensuring excellent performance in industries such as electronics, energy, and healthcare.
Conclusion:
Powder atomizer plants have transformed the landscape of powder production, providing precise control over particle characteristics and enabling the creation of powders tailored to specific industry requirements. These advanced facilities have empowered industries with high-quality powders for additive manufacturing, powder metallurgy, coatings, ceramics, and various other applications. The continuous advancement of powder atomization technology promises further innovation and a limitless range of possibilities for powdered materials in the future.